Form, Use and Meaning
In this package we will look at how to talk or write about the future using will, going to and the present continuous tense (eg. I am meeting my friend this evening). You will revise how to form these tenses and when to use them.
Form of will Future

Use of will Future
- a spontaneous decision
example: (the phone rings) Okay, I’ll get it.
- an opinion, hope, uncertainty or assumption regarding the future
example: He will probably come back tomorrow.
- a promise
example: Don’t worry. I will always be there for you.
- an action in the future that cannot be influenced
example: The democrats will win with an increased majority.
- conditional clauses type I
example: If there’s a delay, I will let you know.
Signal Words
- in a year, next …, tomorrow
- I think, probably, perhaps
Activity 1
Complete the following passage by typing in the correct future form.
1. Kelvin asked a fortune-teller about his future. Here is what she told him:
Form of going to Future
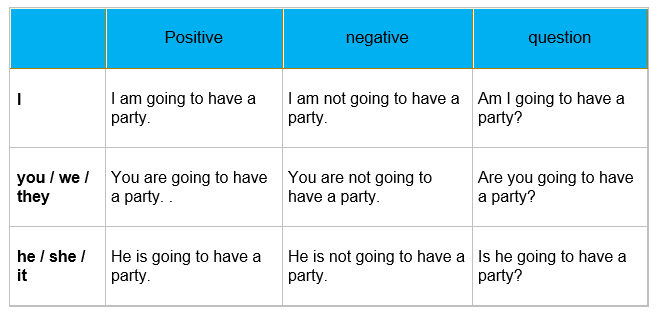
Use of going to Future
- an action in the near future that has already been planned or prepared
example: I am going to work on a kibbutz this summer.
- an action or event in the future for which there is some present evidence
example: Look at those men arguing. I think there’s going to be a fight.
Signal Words
- in one year, next week, tomorrow
Activity 2
Complete the following passage by typing in the correct future form.
Present continuous
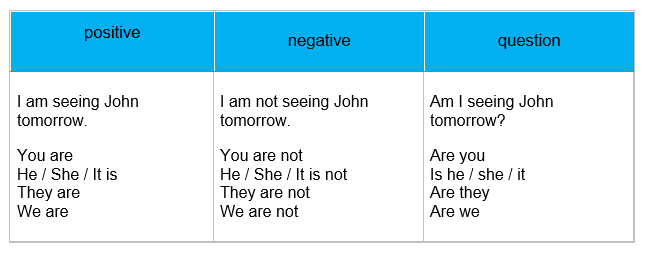
Use of present continuous Future
- an action in the near future that has already been planned or prepared
example: I am flying to Tokyo in the morning.
In the example, we are talking about an arrangement for the near future; the decision to travel to Tokyo was made at some point in the past, the tickets have already been bought and the hotel booked.
Signal Words
- tonight, tomorrow, next Friday, at noon, next week, on Monday, in the summer
Differences and similarities between going to and of present continuous
- For the most part, the two are interchangeable when talking about planned arrangements for the future.
- The only difference that can sometimes be identified is that the present continuous appears to be more definite than going to. Consider these examples:
I’m going to have a party on Saturday.
You’ve decided but haven’t organized anything yet.
I’m having a party on Saturday.
You’ve already bought some of the food and drinks and have already invited lots of people.
- The other key difference is that the present continuous cannot be used to talk about future actions or events where there is some present evidence.
Look at those clouds. I think it’s going to rain. ✓
Look at those clouds. I think it’s raining. X
Activity 3
Complete the following sentences by typing in the correct future form.
Complete the following questions by typing in the correct future form. For each question choose the reason for the future form from the drop down menu.
Now try the quiz again.
1. Read these three sentences and for each one, answer the questions that follow.
a). I’ll have a party on Saturday.
b). I’m going to have a party on Saturday.
c). I’m having a party on Saturday.
Click the tabs to show contents.



